Understanding RefCell in Rust
There are many aspects to the Rust language that are hard to understand at first. Consider the RefCell struct. This gives us "interior mutability"—but what is that, and why do we need it? Suppose we have a struct, and we pass the struct as an immutable reference throughout our program.
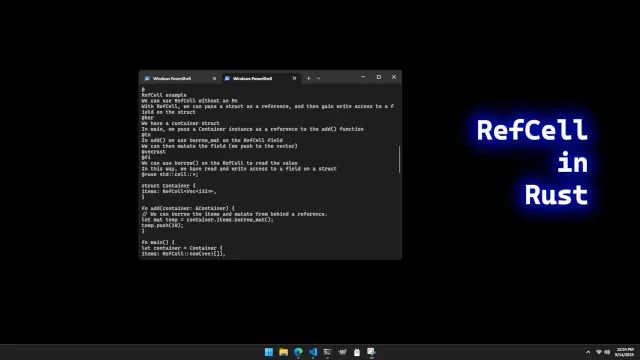
Many parts of our program might use the struct, mostly reading from it. Occasionally, a change to the data in the RefCell is needed. By calling borrow or borrow_mut we can get read access or exclusive write access. RefCell tracks at runtime whether calling borrow or borrow_mut should succeed—if no other uses are active in the program, it will allow the calls.
Some advantages to RefCell include:
borrow_mut (write).mut references everywhere as arguments.For threads, the RwLock struct is the same as RefCell (which cannot be used across threads). Basically the point of RefCell, then, is that we can safely modify a field through an immutable struct reference.